Conflict Minerals
What are "Conflict Minerals"?
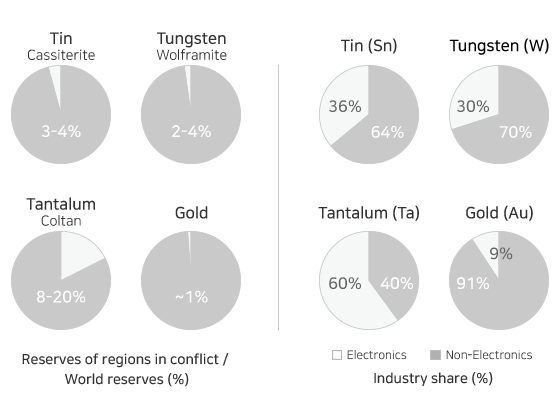
Conflict minerals are minerals mined in conflict regions in Africa (10 countries including the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Central African Republic) and refer to tin, tungsten, tantalum, and gold (hereinafter referred to as '3TG').
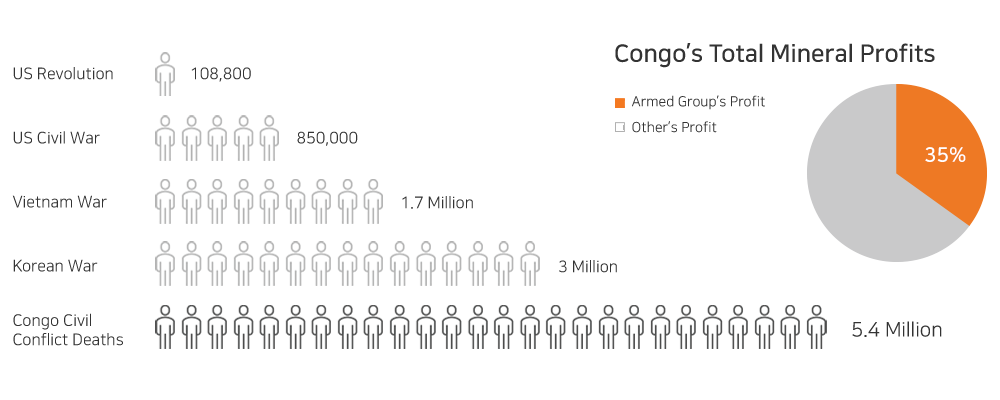
Guerrillas and rebels in this region are mining mineral resources to secure military funds, and in the process, are incurring social problems such as human rights violations, child labor exploitations, and sexual assaults.
Four major minerals (3TG: tin, tungsten, tantalum and gold) mined in these regions have been designated as conflict minerals, mainly by developed nations. In addition, a new regulation in order to prevent money spent on mining from flowing into military funds of rebel armies, named "Conflict Minerals Regulation", has come into effect from 2014.
Conflict Minerals (3TG) : Tin, Tantalum, Tungsten, Gold
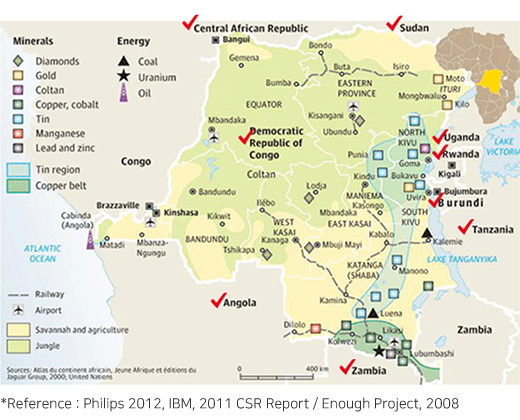
Conflict Areas (10 countries) : DR Congo, Congo, South Sudan, Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, Zambia, Angola, Tanzania, and Central African Republic
Conflict Mineral Deposits in Conflict Regions
JNTC is actively participating in international efforts
to ban the use of conflict minerals.
Regarding conflict minerals that are becoming a global issue, JNTC complies with the relevant laws and regulations and co-responds with domestic and foreign partners and customers for systematic supply chain management, and monitors government policies and support contents to respond to conflict minerals regulations and to build a gradual process for this.
- Using the Conflict Minerals Use Report Questionnaire (EICC Template) provided by EICC-GeSi, we will conduct a thorough investigation of the use of conflict minerals by conducting a survey on the use of conflict minerals for domestic and overseas partners.
- We will confirm and request in writing the submission of a questionnaire on the use of conflict minerals by domestic and overseas partners and a non-use compliance agreement stating that conflict minerals are not used.
- We will make it mandatory to identify the origin and smelter of the conflict minerals of our partners and the origin of the minerals used in the smelters and will work together to comply with conflict minerals regulations.
- We will make it mandatory to identify the origin and smelter of the conflict minerals of our domestic and overseas partners and the origin of the minerals used in the smelters to comply with conflict minerals regulations and will encourage selection of CFS(Conflict-Free Smelter)-compliant minerals.
- We will add cobalt, which is becoming an issue due to human rights issues such as child labor, to the list of conflict materials and respond equally.